- The Daily AI Show Newsletter
- Posts
- The Daily AI Show: Issue #83
The Daily AI Show: Issue #83
...and we are back!

Welcome to Issue #83 and Happy New Year!
Coming Up:
Voice Interfaces Are Forcing a Rethink of AI Interaction
Claude Code and the Rise of Long Running AI Work
CES Showed the Future of Robots, Adoption Is Another Story
Plus, we discuss the CES swerve, Microsoft continues to do good in Indonesia, if we should have AI sanctuaries, and all the news we found interesting this week.
It’s Sunday morning.
AI is already revealing what will be possible in 2026.
What will you build?
The DAS Crew
Our Top AI Topics This Week
Voice Interfaces Are Forcing a Rethink of AI Interaction
Voice based AI tools are getting good enough that typing is no longer the default. Tools like Wispr Flow and Monologue let people speak naturally and let the system clean things up before sending them to a model. For many users, this already covers a large share of daily AI interactions.
That shift sounds small, but it changes how people work with AI in a meaningful way.
When people type, they self edit. When they speak, they think out loud. Voicing surfaces half-formed ideas, detours, corrections, and intuition that never makes it into a written prompt. AI has no trouble handling that. It filters the noise and extracts intent. Humans, on the other hand, are used to conversational pressure that forces concision. AI does not apply that pressure.
This creates a tension. Voice-first AI removes friction and speeds up work, but it can also reinforce habits like rambling, delayed clarity, and over-explanation. The model patiently waits, cleans things up, and returns something coherent. The user never feels the cost of being unclear.
At the same time, voice reveals something valuable. Many decisions are not linear. People often reach clarity by talking through options, revising assumptions, and reacting to their own words. Voice captures that process. Typing usually hides it.
This matters for where AI is heading. If assistants are going to work alongside people, not just answer prompts, they need to observe how decisions actually form. Not just the final instruction, but the path that led there. That includes uncertainty, gut checks, exceptions, and context that never makes it into a formal process.
The next step is personalization. An assistant that knows when to interrupt. When to summarize. When to push for clarity. When to cut someone off and say, I have enough. That kind of behavior is not built into today’s voice tools, but it is clearly where expectations are moving.
Voice-first AI is exposing how much cognitive work happens before a clean decision exists. The systems that learn to support that phase, without reinforcing bad habits, will be the ones people trust most in 2026.
Claude Code and the Rise of Long-Running AI Work
Claude Code is gaining attention for a simple reason: It works. For extended periods of time. On real tasks. Across files, tools, and environments.
The key difference is duration and structure. Claude Code can run for an hour or more without constant human intervention. It breaks a goal into sub tasks, works through them methodically, evaluates its own progress, and keeps going. That alone separates it from most AI tools people use today, which still depend on short prompts and frequent steering.
This is possible because of how the system handles context and recursion. Instead of treating every request as a single prompt response cycle, Claude Code compacts prior work, summarizes what matters, and restarts with a fresh context window while preserving intent. It also uses Skills, reusable instruction blocks that get pulled in only when needed. That keeps token usage low and relevance high.
The result is practical autonomy. You can hand Claude Code a messy folder, a vague goal, or a half built project and let it operate. It can generate files, update code, evaluate outputs, fix errors, and continue without resetting every few minutes. People are already using it to recreate months of engineering work in a single session, not as a final product, but as a working foundation.
Using Claude Code this way does not require that you be an engineer to be a developer. What matters is pattern recognition. Understanding how files relate. Knowing what JSON looks like when it is broken is useful, but if you don’t, just ask Claude. You will learn to read structure even if you cannot write it from scratch. Claude Code lowers the barrier by handling syntax, but it still rewards the people who understand how code systems fit together.
The bigger signal is where this is heading. AI is moving away from chat and toward execution. Tools like Claude Code behave less like explanatory assistants and more like junior teammates who can take ownership of work product. They are not perfect. They still need oversight and direction. But the leap from minutes to hours of sustained effort changes what is possible.
This is about learning how to delegate work to systems that can now carry it forward on their own. That shift is already underway, and Claude Code is one of the clearest examples of what comes next.
CES Showed the Future of Robots, Adoption Is Another Story
CES made one thing clear. Robotics is no longer confined to factories, labs, or research demos. Multiple companies are now targeting the home directly, with designs that favor practicality over spectacle. Wheeled bases instead of legs. Focused task sets instead of general intelligence. Integration with existing home ecosystems instead of standalone novelty devices.
LG’s approach shows this clearly. Rather than offering humanoid walking robots, their design centers on stable movement, limited but useful dexterity, and tight integration with appliances people already own. SwitchBot takes a similar path, aiming for affordability and ecosystem compatibility instead of cutting-edge embodied AI. These systems are not trying to impress. They are trying to fit.
At the same time, industrial robotics is scaling fast. Automotive manufacturers and logistics companies are preparing for tens of thousands of humanoid units per year, with clear use cases and controlled environments. The capital investment is real, and so is the expectation of labor displacement in specific roles. This side of robotics is moving quickly because the value proposition is obvious and the workflows are well defined.
The tension comes when these two worlds meet everyday life. For most people, robotics still feels distant. Laundry still piles up. Recycling still needs sorting. Chores still compete with work, family, and limited attention. Even as the technology advances, many people struggle to see where it fits into their daily routines.
This gap matters. The technology is accelerating, but adoption depends on trust, relevance, and clear value. Devices that quietly reduce friction will win. Systems that demand new habits or constant attention will stall. The next phase of robotics will not be defined by what is possible. It will be defined by what feels useful enough to become invisible.
That is the real challenge for 2026. Not building robots that can do more, but building robots that fit naturally into lives that already feel full.
Just Jokes
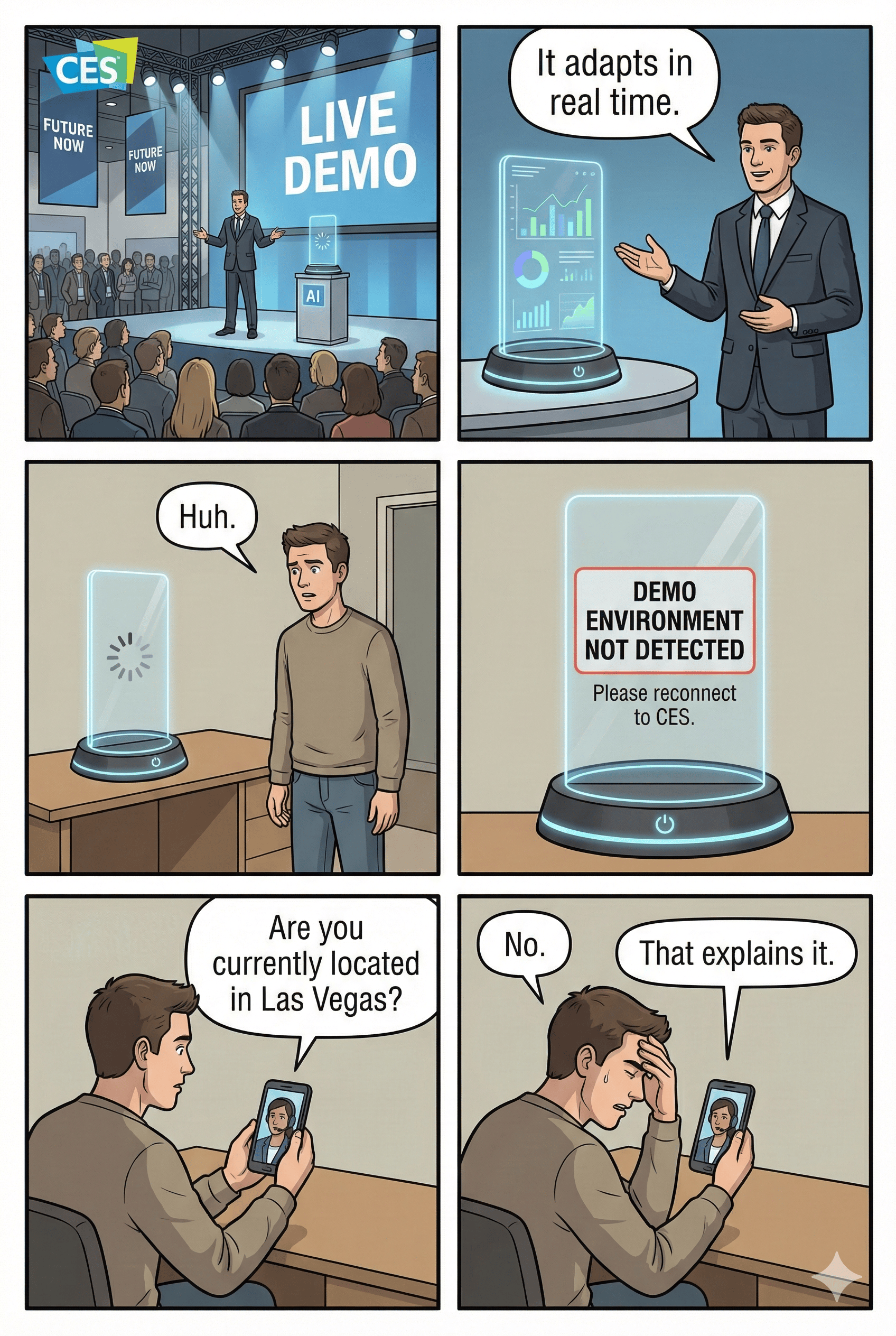
The CES Swerve
AI For Good
Microsoft Indonesia launched the second year of its “Microsoft Elevate Indonesia” program, aiming to train 500,000 certified AI talents by 2026. The initiative has already helped more than 1.2 million people gain AI skills since its start in 2024 and focuses on equipping educators, community leaders, nonprofit professionals, and small business owners with practical AI knowledge. The goal is to expand access to AI education across the country, giving participants tools to build technology solutions that benefit their local communities and accelerate digital transformation.
This Week’s Conundrum
A difficult problem or question that doesn't have a clear or easy solution.
The Analog Sanctuary Conundrum
For most of history, "privacy" meant being behind a closed door. Today, the door is irrelevant. We live within a ubiquitous "Cognitive Grid"—a network of AI that tracks our heart rates through smartwatches, analyzes our emotional states through city-wide cameras, and predicts our future needs through our data. This grid provides incredible safety; it can detect a heart attack before it happens or stop a crime before the first blow is struck. But it has also eliminated the "unobserved self." There is no longer a space where a human can act, think, or fail without being nudged, optimized, or recorded by an algorithm. We are the first generation of humans who are never truly alone, and the psychological cost of this constant "optimization" is starting to show in a rise of chronic anxiety and a loss of human spontaneity.
The conundrum:
As the "Cognitive Grid" becomes inescapable, do we establish legally protected "Analog Sanctuaries"? We are talking refuges, entire neighborhoods or public buildings where all AI monitoring, data collection, and algorithmic "nudging" are physically jammed and prohibited. Or do we forbid these zones because they create dangerous "black holes" for law enforcement and emergency services, effectively allowing the wealthy to buy their way out of the social contract while leaving the rest of society in a state of permanent surveillance?
Want to go deeper on this conundrum?
Listen to our AI hosted episode

Did You Miss A Show Last Week?
Catch the full live episodes on YouTube or take us with you in podcast form on Apple Podcasts or Spotify.
News That Caught Our Eye
Details Emerge on OpenAI and Jony Ive’s Screenless AI Device
New reporting surfaced around OpenAI’s hardware project with Jony Ive, codenamed Gumdrop. The device appears to be a pen-like input tool with a microphone and camera but no screen. Users could scan handwritten notes or documents and interact with ChatGPT through voice and connected earbuds rather than a display. The design aims to avoid competing directly with smartphones and reduce social friction around camera-equipped wearables.
Deeper Insight:
OpenAI is betting that post-smartphone AI hardware will center on input, not output. If successful, this shifts interaction away from screens and toward ambient, voice-first workflows tied tightly to a single assistant.
Yann LeCun Criticizes Meta Leadership and Scale AI Deal
In a candid Financial Times interview, Yann LeCun criticized Meta’s decision to elevate Alexander Wang after the Scale AI acquisition. He described the move as destabilizing and suggested it contributed to internal dysfunction and talent attrition. LeCun has since moved on to build a new company focused on world models.
Deeper Insight:
Leadership turbulence matters more than compensation at the frontier. As AI talent becomes financially independent, stability and clarity increasingly determine where top researchers choose to work.
LeCun Claims Meta Fudged Llama 4 Benchmarks
LeCun also alleged that Meta AI researchers manipulated benchmark results for Llama 4, contributing to Mark Zuckerberg’s loss of confidence in the GenAI organization. The claims add to a growing pattern of skepticism around benchmark-driven qualification of models.
Deeper Insight:
Benchmarks are losing credibility as a primary signal of progress. Internal trust and real world performance now matter more than leaderboard positioning.
Pickle AI Glasses Spark Vaporware Debate
A startup called Pickle unveiled AI glasses claiming superior battery life, weight, and capabilities compared to Meta Ray Ban glasses, despite limited funding. Industry veterans publicly challenged the feasibility of the specs, calling the product vaporware. Pickle’s CEO responded by releasing prototype footage, detailed counterarguments, and accepting a public challenge to ship working hardware by Q2 2026.
Deeper Insight:
The wearable AI space is entering a hype correction phase. Extraordinary claims now trigger immediate technical scrutiny, especially when startups promise to outperform incumbents with far fewer resources.
Anthropic Claude Code Solves Year Long Google Engineering Problem in One Hour
A Google principal engineer reported that Anthropic’s Claude Code generated a distributed agent orchestration system in about an hour. Her team had been working on the same problem internally for nearly a year. She credited Claude’s agent harness as a key differentiator.
Deeper Insight:
Agent coordination frameworks are becoming force multipliers. The value is no longer just the model, but how well multiple agents plan, test, and execute together.
Anthropic to Purchase One Million Google TPUs
Anthropic plans to buy roughly one million Google designed TPU v7 chips from Broadcom rather than renting compute. This move signals a shift toward owning dedicated AI infrastructure and building Anthropic-operated data centers.
Deeper Insight:
Model labs are becoming infrastructure companies. Owning chips and data centers reduces long term cost volatility and weakens dependence on cloud providers.
Researchers Propose Science Context Protocol Built on MCP
Researchers from Shanghai AI Lab proposed extending Anthropic’s Model Context Protocol into a Science Context Protocol. The system would add experimental metadata management and centralized coordination for global scientific collaboration.
Deeper Insight:
AI coordination standards are expanding beyond tools into domains like science. Shared protocols could accelerate research by reducing friction between teams, models, and experiments.
Stanford Researchers Introduce Dream2Flow for Robot Training
Stanford researchers released Dream2Flow, a framework that trains robots using videos by focusing on object movement rather than subject human actions. The system converts video scenes into object-centric three dimensional motion representations that robots can adapt to their own bodies.
Deeper Insight:
Robot learning is shifting from imitation to abstraction. Teaching robots how objects move, not how humans move, makes training transferable across platforms and form factors.
Brookfield Expands Into AI Data Center and Cloud Infrastructure
Brookfield is building AI focused data centers in regions including France, Qatar, and Sweden. The initiative leverages its access to land, power, and capital, and has already impacted market perceptions around AWS dominance.
Deeper Insight:
AI infrastructure is no longer the exclusive domain of hyperscalers. Asset managers with capital and physical resources are emerging as serious competitors in sovereign and industrial AI compute.
Concerns Rise Over AI-Generated War and Crisis Footage
The discussion highlighted growing confusion around AI-generated and enhanced video during real world geopolitical events. Multi-angle AI video generation and enhancement now make it difficult to verify authenticity in breaking news situations.
Deeper Insight:
Synthetic media is collapsing the trust window during crises. Verification will increasingly rely on provenance systems, trusted networks, and collective validation rather than visual inspection.
Nvidia Open Sources Alpamayo Reasoning Model for Autonomous Vehicles
Nvidia announced Alpamayo, an open sourced vision language action model designed for autonomous driving. Unlike traditional systems trained only on simulations and edge cases, Alpamayo reasons through novel scenarios step by step and can explain its decisions in natural language. The system separates perception from reasoning and is designed to handle unexpected real world situations.
Deeper Insight:
Explainability is the missing layer in autonomous systems. By allowing vehicles to reason and articulate why they act, Nvidia addresses trust, safety, and regulatory concerns that have stalled wider adoption of self driving technology.
Mercedes Benz to Ship Vehicles With Nvidia Alpamayo in Q1 2026
Mercedes Benz confirmed that its upcoming CLA model will ship with Nvidia’s full autonomous driving stack, including Alpamayo, as early as the first quarter of 2026. The vehicle will offer Level 2 autonomy powered by Nvidia hardware and software, positioning Mercedes as a direct competitor to Tesla and Waymo.
Deeper Insight:
This is a major shift in the autonomous market. Instead of vertical integration like Tesla, Mercedes is betting on a best-in-class partner stack, accelerating deployment timelines and lowering development risk.
Lego Unveils SmartPlay Bricks With Embedded Sensors and AI
Lego revealed SmartPlay, a new platform of sensor-packed bricks that respond dynamically to play without screens, apps, or internet connectivity. Each standard two-by-four stud brick contains a custom ASIC, accelerometers, magnetometers, proximity sensing, audio output, and near field communication. The first release will be Star Wars themed sets launching in March.
Deeper Insight:
AI toys are moving from gimmicks to embedded intelligence. Lego is turning physical play into a reactive system, laying the groundwork for mass market AI experiences that do not feel like technology at all.
Researchers Create Fully Autonomous Microscopic Robots
Teams from the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Michigan developed microscopic robots small enough to balance on a fingerprint ridge. The robots sense temperature, follow paths, make decisions, and move using electrical field manipulation rather than mechanical parts. This marks the first fully autonomous robots at this miniature scale.
Deeper Insight:
Micro-robotics crosses a critical threshold here. Once robots can sense, decide, and act at microscopic scales, applications in medicine, manufacturing, and environmental monitoring expand dramatically.
LG Introduces Cloid, a Consumer-Ready Home Robot Platform
LG announced Cloid, an embodied AI home robot designed for household chores. The robot uses a wheeled base, articulated arms, vision systems, and autonomous navigation to handle tasks like folding laundry, loading dishwashers, organizing objects, and interacting with smart appliances. LG positions Cloid as part of its broader zero labor home vision.
Deeper Insight:
LG’s advantage is not cutting edge robotics research, but manufacturing scale and consumer trust. Home robots that integrate directly with appliances may reach households faster than humanoids built by startups.
SwitchBot Reveals Onero H1, an Affordable Home Robot Butler
SwitchBot announced Onero H1, a humanoid style home robot priced under five thousand dollars. The robot focuses on upper body manipulation mounted on a wheeled base and integrates tightly with SwitchBot’s existing smart home ecosystem, including locks, curtains, thermostats, and appliances.
Deeper Insight:
Affordability signals a shift from demos to real products. By avoiding bipedal walking and focusing on practical chores, SwitchBot is optimizing for deployment rather than spectacle.
Boston Dynamics Atlas Enters Mass Production for Manufacturing
Boston Dynamics confirmed plans to mass produce its Atlas humanoid robot at a Hyundai-backed facility capable of producing thirty thousand units annually by 2028. Initial deployments will focus on automotive and industrial manufacturing environments rather than homes.
Deeper Insight:
Humanoid robots will scale first in factories, not living rooms. Manufacturing provides controlled environments, clear ROI, and immediate labor replacement opportunities.
Claude Code Plugin Popularizes “Ralph” Agentic Loop Workflow
Developers are adopting a Claude Code plugin known as Ralph, which repeatedly retries tasks until completion without human intervention. The approach allows AI agents to iterate through failures autonomously, making it useful for coding, research, operations, and workflow automation.
Deeper Insight:
Agentic value is shifting from intelligence to persistence. Systems that retry relentlessly until success unlock automation for tasks that previously required constant supervision.
World Labs Demonstrates Physics Accurate World Models at CES
World Labs, led by Fei Fei Li, demonstrated Marble, a system that generates persistent three dimensional environments from text, images, and video. The demo recreated a physics-consistent version of Las Vegas in real time, designed for robotics training and simulation without massive real world data collection.
Deeper Insight:
World models reduce the cost of robotics training dramatically. When robots can learn inside accurate simulated worlds, physical deployment accelerates without relying on endless real world trials.
DeepSeek Adds Interleaved Thinking and Surpasses 130 Million Monthly Users
DeepSeek rolled out an interleaved thinking feature that blends reasoning steps directly into multi step research workflows instead of separating thinking from response generation. The system evaluates credibility between actions as it goes. At the same time, DeepSeek reported rapid user growth, reaching roughly 132 million monthly active users in December, up from about 34 million earlier in the year.
Deeper Insight:
Recursive and interleaved reasoning is becoming a clear pattern across competitive models. DeepSeek’s growth shows that being “good enough and cheap” can drive massive adoption even without leading frontier benchmarks.
Prominent Mathematician Criticizes LLMs as Useless for Pure Math
Renowned mathematician Joel David Hamkins publicly criticized large language models for mathematical research, calling their outputs unreliable and resistant to correction. He argued that confident but incorrect reasoning makes them unusable for serious proof work.
Deeper Insight:
General purpose language models still struggle in domains that demand formal verification. This gap is pushing the field toward domain-specific architectures rather than bigger general models.
Axiom Math Raises 64 Million Dollars to Build a Proof-First AI Mathematician
Startup Axiom Math, founded by a former Stanford student, raised a 64 million dollar seed round to build an AI system focused exclusively on mathematics. Its architecture couples language models with formal proof engines and verification systems, avoiding next token prediction hallucinations and preventing jailbreak style misuse.
Deeper Insight:
This reflects a broader shift toward constrained, verification driven AI. In high stakes domains, correctness matters more than conversational flexibility.
Stanford Releases SleepFM to Predict Over 130 Health Conditions From Sleep Data
Stanford researchers introduced SleepFM, a foundation model trained on more than 600,000 hours of sleep data from 65,000 participants. The model analyzes brain waves, heart activity, breathing, and muscle signals to predict over 130 health conditions from a single night of sleep.
Deeper Insight:
Health AI is moving upstream into early detection. Sleep data is becoming one of the richest signals for identifying long term health risks before symptoms appear.
Withings Unveils BodyScan II, a Medical Grade AI Health Scale
At CES, Withings announced BodyScan II, a smart scale that performs a 90 second scan and measures over 60 biomarkers related to cardiovascular health, cellular composition, metabolic efficiency, and vascular age. The device includes ECG, impedance cardiography, and bio-impedance spectroscopy and costs around 600 dollars, with a subscription for analytics.
Deeper Insight:
AI powered home diagnostics are compressing clinical testing into consumer devices. Preventive health monitoring is shifting from hospitals to bathrooms.
CES Showcases Rise of Cognitive Assistance Wearables
Multiple companies introduced AI wearables focused on cognitive assistance rather than screens. Highlights included smart rings and pendants that record conversations, transcribe speech in over 100 languages, identify speakers, and store encrypted notes for later recall.
Deeper Insight:
Wearables are evolving from fitness tracking to memory augmentation. Cognitive offloading is emerging as a mainstream use case for AI hardware.
Instagram CEO Signals Shift Toward Authenticity Over Polished Content
Instagram leadership emphasized that future creator success will rely less on production quality and more on authentic presence, consistent identity, and community trust. As feeds surface isolated posts rather than full profiles, social proof and recognizable patterns matter more than visual perfection.
Deeper Insight:
AI commoditizes polish. Human credibility, history, and relationships are becoming the real differentiators in content and commerce
LMArena Reaches 1.7 Billion Dollar Valuation Four Months After Launching Enterprise Evaluations
LM Arena secured a reported 1.7 billion dollar valuation driven by its new enterprise product, AI Evaluations. The offering sells structured, real world human feedback and performance analysis to model developers and enterprises. While the public leaderboard remains free, companies can now pay to benchmark models using LM Arena’s large scale preference and comparison data.
Deeper Insight:
Evaluation data has become a monetizable asset. As benchmarks lose credibility, real human preference data at scale becomes one of the most valuable feedback loops in model development.
Google DeepMind Partners With Boston Dynamics on Humanoid Robotics
Google DeepMind announced a partnership with Boston Dynamics to advance humanoid robotics. The collaboration combines DeepMind’s reasoning and planning systems with Boston Dynamics’ Atlas platform, which is backed by Hyundai’s manufacturing and industrial footprint. The focus is on adaptable, multi-task robots rather than single purpose automation.
Deeper Insight:
Humanoid robotics is shifting from demos to deployment. Intelligence plus manufacturing scale matters more than novelty, and factory floors are emerging as the first real proving ground.
Google Classroom Adds AI Generated Podcast Style Lessons
Google released a new Gemini powered feature in Google Classroom that allows teachers to generate podcast style audio lessons. Educators can control emphasis and learning objectives, making the content more structured than general audio generation tools like NotebookLM.
Deeper Insight:
Education is moving toward multimodal learning by default. Audio, text, and visuals are converging into flexible lesson formats that adapt to different learning styles.
Ford Announces In House AI Voice Assistant and Level 3 Autonomy Timeline
Ford revealed plans to launch an in house AI voice assistant later this year and to introduce Level 3 hands-free autonomous driving in 2027. The company is pulling more software development in house to control the full vehicle experience rather than relying on third party platforms.
Deeper Insight:
Automakers are becoming software companies by necessity. Control over AI systems is emerging as a core competitive advantage, not a feature add on.
ChatGPT Health Expands With Encrypted Personal Health Data Support
OpenAI introduced ChatGPT Health, allowing users to upload and analyze personal health data such as lab results and trends inside a dedicated encrypted environment. The system supports longitudinal analysis while keeping health data isolated from general training.
Deeper Insight:
Health data creates long term platform stickiness. Assistants that understand personal health history may become difficult to replace, even if competing models improve faster.
Cursor Introduces Dynamic Context to Reduce Token Usage in Long Running Tasks
Cursor released Dynamic Context Discovery, a system that selectively loads only relevant information during inference. The approach treats tool outputs and sessions as retrievable files rather than static prompt context, reducing cost and enabling longer autonomous runs.
Deeper Insight:
Efficiency is becoming as important as intelligence. Smarter context management allows agents to work longer, cheaper, and with less user supervision.
Claude Code Ecosystem Expands With Skills, Bootstrap Guides, and Autonomous Loops
The Claude Code ecosystem continues to grow with new components like opinionated initialization and style guides, reusable skills, and autonomous retry loops such as Ralph. These additions allow Claude Code to operate for extended periods without human intervention while maintaining structure and reliability.
Deeper Insight:
Agentic systems are maturing into toolchains, not single products. Persistence, structure, and orchestration now matter more than raw model capability.
OpenAI Acquires Convogo to Expand Enterprise Leadership Tools
OpenAI acquired Convogo, a company focused on leadership assessment and feedback software. While the Convogo product itself is not expected to continue independently, the team will be integrated into OpenAI’s enterprise efforts to expand AI-driven management, evaluation, and organizational tooling.
Deeper Insight:
OpenAI is building a broad enterprise suite, not just a model API. Leadership evaluation, coaching, and organizational insight are emerging as high value AI use cases inside large companies.
Google Gemini Reaches Over 20 Percent of Global Chat Traffic
Google’s Gemini platform now accounts for more than 20 percent of global AI chat traffic. The growth reflects tighter integration across Google products and improved model performance. Alphabet recently surpassed Apple to become the world’s second most valuable company, trailing only Nvidia.
Deeper Insight:
Distribution matters as much as model quality. Google’s ability to embed Gemini across Search, Gmail, Docs, and Chrome gives it an advantage that standalone AI apps cannot easily replicate.
Google Prepares AI Native Inbox Experience for Gmail
Google previewed plans for an AI native inbox that goes beyond the current Gemini side panel in Gmail. The new experience is expected to synthesize email threads, meetings, documents, and calendar context into higher level summaries and actions, while remaining supported by advertising.
Deeper Insight:
Email is shifting from message management to intent management. AI inboxes that understand relationships, history, and upcoming commitments could fundamentally change how knowledge workers interact with communication tools.
Anthropic Valuation Climbs to 350 Billion Dollars After New Funding Round
Anthropic completed a new funding round valuing the company at approximately 350 billion dollars. The raise follows strong momentum around Claude Code and enterprise adoption, positioning Anthropic alongside OpenAI and Google as one of the three dominant AI labs.
Deeper Insight:
Capital is consolidating around a small number of frontier labs. Investor confidence is increasingly tied to agent frameworks and enterprise deployment, not just benchmark leadership.
Sakana AI and MIT Release Digital Red Queen Research on Self Improving Code
Sakana AI, in collaboration with MIT, published research on Digital Red Queen dynamics using an adversarial code evolution environment inspired by the classic Core War framework. Autonomous programs repeatedly evolved, competed, and improved until converging on similar optimal strategies.
Deeper Insight:
Recursive self improvement appears to have natural convergence points. This suggests that while autonomous evolution can accelerate progress, it may also limit diversity once optimal strategies dominate.
Pathways Introduces Post Transformer Brain Inspired AI Architecture
Pathways revealed a new AI architecture designed to move beyond transformers. The system uses graph based dynamics inspired by human cognition rather than static training runs. The approach aims to create adaptive, continuously learning systems rather than frozen models.
Deeper Insight:
Transformer scaling may not be the final path to general intelligence. Brain inspired architectures could unlock adaptability and learning behaviors that current LLMs struggle to achieve.
