- The Daily AI Show Newsletter
- Posts
- The Daily AI Show: Issue #71
The Daily AI Show: Issue #71

Welcome to Issue #71
Coming Up:
The Robotics Race: Google, Meta, and Nvidia Take Different Paths
The Great AI Compute Traffic Jam
Why Claude Code Could Reshape Productivity
Plus, we discuss Sora 2, what preemptive AI consent could mean, new models that look into the future to help prevent seizures, and all the news we found interesting this week.
It’s Sunday morning.
Brian’s local Publix grocery store currently has both firewood and pool toys outside for sale.
You know what that means….
OK, neither do we.
But we do know it is time to cozy up to this week’s AI newsletter.
Enjoy!
The DAS Crew - Andy, Beth, Brian, Eran, Jyunmi, and Karl
Why It Matters
Our Deeper Look Into This Week’s Topics
The Robotics Race: Google, Meta, and Nvidia Take Different Paths
The next wave of AI is not staying on screens. It is moving into the physical world through robots that can reason, adapt, and act. Three major strategies are now emerging, each led by a different tech giant.
Google DeepMind has introduced Gemini Robotics, a “brain in a box” model built to power any robot. The system splits into two parts: a reasoning model that plans and problem-solves, and an action model that executes movements. The reasoning brain will be available broadly through Gemini’s API, while the action model is limited to partners. The focus is on transfer learning, a skill learned by one robot can be applied seamlessly to another with a different form factor.
Meta is taking what it calls an “Android for robots” approach, aiming to build the operating system layer rather than the hardware. This strategy mirrors its early bet on open-source AI models like LLaMA. By creating a common foundation, Meta hopes to attract developers and hardware makers to build on top of its platform, avoiding the costly mistakes it made with development of VR hardware.
Nvidia is going vertical. Its Isaac platform combines realistic world simulation for robot training (Isaac SIM), reinforcement learning environments (Isaac Lab), their foundation model for robotic reasoning (Groot N1), and specialized processors for mobile, untethered robots (Jetson Thor). This one-stop ecosystem allows developers to design, train, test, and deploy robotic systems with both the software brains and the compute hardware power included. Nvidia’s has an edge in synthetic data: millions of motions and interactions generated in simulation, reducing the need for costly real-world training.
Tesla has their comprehensive vertical but proprietary Optimus robotics system, Apple is working on something, and startups like Figure also loom in the background, but the strategic battle lines are clearest with Google, Meta, and Nvidia’s approaches. Whether the dominant platform of the future belongs to a universal brain, an open operating system, or a vertically integrated stack will shape how fast robotics moves from research labs to homes, factories, and disaster zones.
WHY IT MATTERS
Different Models, Same Goal: A universal brain, an operating system, and a full-stack platform each point to different visions of the market-space for robot intelligence.
Transfer Learning Is Critical: Google’s approach shows how robots may one day share skills instantly across form factors.
Synthetic Data Accelerates Progress: Nvidia’s simulated training allows robots to practice in hours what would take humans months to teach.
Operating Systems Win Ecosystems: Meta is betting that a shared OS platform will attract the broadest developer community.
Robots Will Be Ubiquitous: From disaster relief to construction to household chores, these strategies could decide how quickly and how uniformly robots become part of daily life.
The Great AI Compute Traffic Jam
AI’s biggest bottleneck is no longer algorithms. It is the physical infrastructure that moves data inside chips and across data centers as billions of users demand inference processing and image generation. Today’s GPUs, TPUs and CPUs are like skyscrapers in a city with outdated roads. The chips themselves are powerful, but the copper wiring that carries electrons between components is slow, hot, and inefficient. As a result, 75% of the energy inside data centers is consumed just moving information back and forth and around, the rest is mostly the algorithmic calculations.
The solution now gaining momentum is photonics, replacing copper and electrons with silicon and laser light. Light-based interconnects between components can move data at near the speed of light, with less heat and far less energy loss than copper. Companies like Intel, Nvidia, AMD, and startups such as Lightmatter are racing to integrate these technologies, from today’s pluggable optics at the edge of server racks, to co-packaged optics that bring photonic interconnects directly into the chip package, to the longer-term goal of full photonic computing where even the math is done with light.
The shift will not only cut energy use, it will also unlock new possibilities. Imagine real-time processing of global climate data, instantaneous medical imaging analysis, or fully autonomous systems reacting in microseconds. These are currently time-constrained by data movement, not model intelligence. By redesigning chips around light instead of copper, the AI “traffic jam” could give way to breakthroughs in speed and efficiency that feel impossible today.
WHY IT MATTERS
Energy Efficiency Jumps: Moving from electrons to photons reduces wasted energy and heat inside chips and across the processor package.
Latency Collapses: Data transfer distances drop from inches to millimeters, enabling more instantaneous responses.
Industry Leaders Are Racing: Intel, Nvidia, AMD, and startups are betting on optics as the next competitive frontier.
Future-Proof Data Centers: Facilities built today must plan for upgrades to photonics or risk costs of early obsolescence.
New AI Applications Open Up: From digital twins of Earth to advanced medical diagnostics, light-based chips and systems expand what AI can compute with realism in real time.
Why Claude Code Could Reshape Productivity
By running inside tools like VS Code or Cursor, Claude Code acts as a local coding commander for both software application development and everyday business tasks. Instead of simply generating code snippets, Claude Code can actively create folders, move files, draft emails, and even chain workflows across multiple SaaS platforms through MCP servers, becoming an agentic assistant lodged in your own computing environment.
The real power comes when Claude Code is paired with MCP integrations. Through Zapier, it can instantly connect with Salesforce, Asana, HubSpot, Outlook, Google Drive, and thousands of other services, handling tasks like calling on tools and services, sending messages, updating records, or consolidating reports. Developers and business teams can also add third-party MCPs directly from GitHub, expanding functionality with analytics, scraping, or automation. Security remains a concern here, as unvetted MCPs may introduce risks like prompt injections. Enterprise-focused tools such as MCP Manager are beginning to address this gap, offering regulated environments for safer deployments.
Perhaps the most transformative feature is agent creation. Claude Code can generate specialized agents on demand, like an invoice consolidator, payroll assistant, or client emailer. Once created, these agents live inside your environment and can be invoked with simple slash commands. Combined with MCP connections, this turns Claude Code into a practical operating system for work. One that can coordinate multiple agents, run tasks across files and folders, and connect with cloud tools in real time.
For IT leaders, the implications are double-edged. On one hand, Claude Code shows how AI can unlock productivity by eliminating repetitive tasks. On the other, it gives users direct power to integrate and automate processes without centralized oversight, raising questions about governance, compliance, and security.
WHY IT MATTERS
From Coding to Operations: Claude Code is evolving from code generation to full business workflow management.
Agents Multiply Productivity: Users can spin up specialized agents for tasks like reporting, payroll, or client communication.
Zapier Expands Reach: A single MCP server opens access to thousands of SaaS tools, from analytics to CRMs.
Security Is the Tradeoff: Third-party MCPs offer power but introduce risks, creating demand for enterprise-level safeguards.
A New Work OS: For many, Claude Code is becoming less an IDE plugin and more a personal operating system for daily work.
Just Jokes
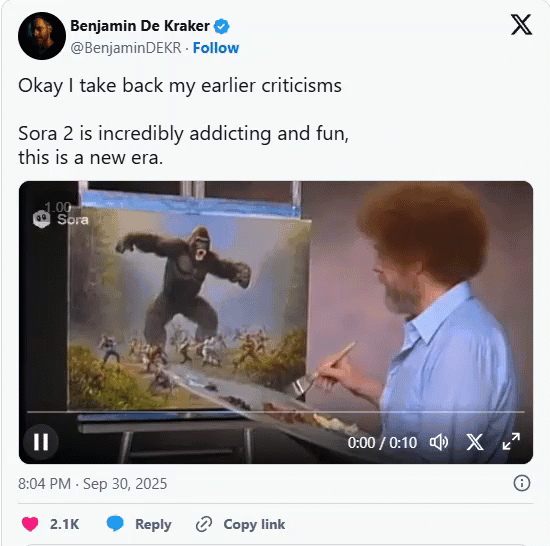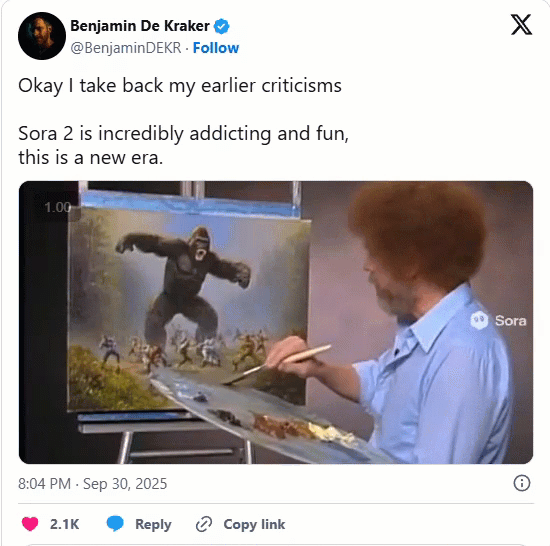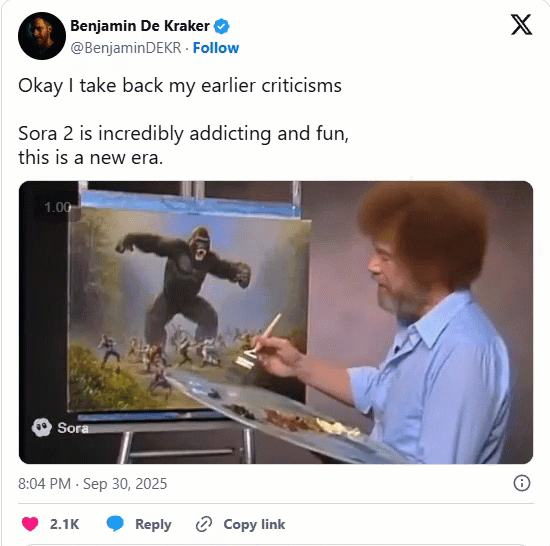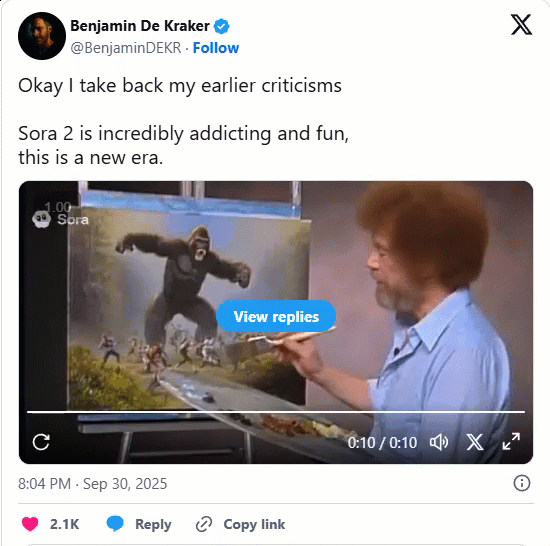
One of our current favorite Sora 2 creations.
Bob Ross paints a gorilla fighting 100 men
Did you know?
Researchers at UC Santa Cruz created a temporal future-guided deep learning model that improves seizure prediction for people with epilepsy. Traditional models often struggle because brain activity is highly dynamic, but this system trains on progressions to future data patterns and then applies those lessons to current brain signal observations. By learning how such signals evolve, the model can recognize the subtle early markers that usually get missed.
In trials, the approach significantly boosted accuracy in forecasting seizures, reducing false alarms and improving the ability to anticipate episodes in real time. This means doctors could intervene earlier and patients could gain more reliable warnings. The goal is to help people better manage daily life, limit unexpected seizures, and support the development of treatments that respond before an episode begins.
The team also sees potential for applying the same method to other time-series health data, such as heart monitoring or early detection of neurodegenerative disorders.
This Week’s Conundrum
A difficult problem or question that doesn't have a clear or easy solution.
The AI Consent Conundrum
Your watch trims a micro dose of insulin while you sleep. You wake up steady and never knew there was a decision to be made hours ago. Your car eases off the gas a block early and you miss a crash you never saw. A parental app softens a friend’s harsh message so a fight never starts. Each act feels like care arriving before awareness, the kind of help you would have chosen if you had the prescience to choose.
Now the edges blur. The same systems mute a text you would have wanted to read, raise your insurance score by quietly steering your routes, or nudge you away from a protest that might have mattered. You only learn later, if at all. You approve some outcomes after the fact, you resent others, and you cannot tell where help ends and meddling shaping begins.
The conundrum
When AI acts before we even know a choice exists, what counts as consent? If we would have said yes, does approval after the fact make the intervention legitimate, or did the loss of that decision moment matter?
If we would have said no, was the harm averted worth taking our agency away, and did the pattern of unseen nudges change who we became over time?
The same preemptive act can be both protection and control, depending on timing, visibility, and whose interests set the default.
How should a society draw that line when the line is only visible after the decision has already been made?
Want to go deeper on this conundrum?
Listen to our AI hosted episode
News That Caught Our Eye
Anthropic Releases Claude Sonnet 4.5
Anthropic introduced Claude Sonnet 4.5, its most capable and aligned model yet. The company claims state-of-the-art performance in coding and computer use, continuing its push to make Claude a top-tier developer assistant and general-purpose AI.
Deeper Insight:
Anthropic is aiming to solidify Claude’s position as the go-to for coding and structured tasks. By emphasizing alignment alongside capability, it’s trying to differentiate from rivals that have faced criticism for unpredictable outputs.
OpenAI and DeepMind Alumni Launch Periodic Labs with $300M
Periodic Labs, founded by former OpenAI and DeepMind researchers, raised $300 million from backers including Andreessen Horowitz, Nvidia, Jeff Bezos, and Eric Schmidt. The startup wants to accelerate scientific discovery with AI-run “self-driving labs,” highly-automated research facilities combining humans with advanced AI and robotics, starting with the hunt for new superconductors.
Deeper Insight:
This represents a major bet on AI for materials science. By combining AI models with robotic experimentation, Periodic Labs hopes to accelerate discoveries that could reshape energy, computing, and medicine.
Los Alamos National Lab Introduces Thor AI for Physics Modeling
Scientists at Los Alamos developed Thor AI, an AI framework that solves the century-old problem of configurational integrals, which model particle interactions. Previously requiring thousands of hours of supercomputing, Thor AI can now complete the work in seconds.
Deeper Insight:
This breakthrough has immediate applications in materials science and atomic research. Public labs advancing this open-source technology means private startups like Periodic Labs may quickly incorporate it, driving faster innovation across multiple industries.
OpenAI Expands Sora with Physics-Faithful Video and Social App
OpenAI released updates to Sora 2 , enhancing its video generator with more accurate physics and sound. They also launched an invite-only Sora social app, modeled after TikTok, that allows users to post AI-generated clips and human “cameos” with verified likenesses.
Deeper Insight:
This is a strategic move into social media. By pairing Sora’s generation tools with a social-sharing platform, OpenAI is directly challenging TikTok and Meta for user attention in the short-form video space.
Deepfakes Hit Politics and Celebrity Culture
Deepfakes remain a growing problem. Recent examples include Elon Musk used in crypto scams, Scarlett Johansson in fabricated political statements, and Chuck Schumer and Hakeem Jeffries depicted in offensive caricatures, which were posted by Donald Trump on Truth Social.
Deeper Insight:
As deepfakes become easier to produce and harder to debunk, political misinformation and reputational attacks are escalating. Regulatory and technical countermeasures will be critical as elections approach.
Nothing Phone 3 Launches AI App Generation Feature
The new Nothing Phone 3 allows users to generate custom apps on-device with AI prompts, bypassing traditional app stores. Early demos showed users creating widgets and custom tools instantly and publishing them for others to remix.
Deeper Insight:
If successful, this could disrupt app distribution models. On-device AI app creation reduces reliance on centralized platforms like Google Play, while empowering niche communities to build their own tools.
X.ai Announces Grokpedia, an AI Wikipedia Competitor
Elon Musk’s xAI announced Grokpedia, an AI-driven alternative to Wikipedia that uses Grok models to automatically detect and correct inaccuracies in online content to create more reliable encyclopedic information.
Deeper Insight:
While ambitious, Grokpedia faces credibility challenges. Wikipedia thrives on community moderation, and Grok has already been criticized for rewriting content inaccurately. Trust will be the biggest hurdle.
CoreWeave Expands with Meta and OpenAI Infrastructure Deals
CoreWeave secured a $14.2 billion deal with Meta and expanded its existing $6.5 billion partnership with OpenAI. The company specializes in buildout and provisioning of GPU cloud infrastructure and is now seen as a central player in AI data center expansion.
Deeper Insight:
CoreWeave’s rise reflects the insatiable demand for compute. By positioning itself as the backbone provider for leading labs, it is becoming as essential to AI infrastructure as chipmakers themselves.
Amazon Launches Alexa Plus and Expands Sports AI with NBA Deal
Amazon announced Alexa Plus, a more advanced AI version of its assistant, which will be pre-installed on all new Echo and Fire devices. At the same time, AWS struck a partnership with the NBA to power AI-driven data insights and in-game features.
Deeper Insight:
Amazon is doubling down on consumer AI and sports analytics. Alexa Plus aims to revive flagging enthusiasm for voice assistants, while sports partnerships push AWS deeper into mainstream entertainment.
Lovable and Bolt Simplify SaaS App Dev and Deployment
Lovable and Bolt released new features that streamline backend integration, authentication, and payment processing for AI-generated applications. Lovable now handles user databases automatically, while Bolt focuses on enterprise-scale connectors.
Deeper Insight:
These tools lower the barrier for non-developers to create custom business or consumer apps. While not aimed at mass-market product or SaaS startups, they could revolutionize how small teams and local businesses build tailored software.
Quantum Computing Advances: UNSW and Caltech Push Boundaries
UNSW researchers demonstrated quantum chips with 99% error correction using existing silicon processes, while Caltech set a record by creating a 6,100-qubit system using neutral atom qubits manipulated by laser tweezers.
Deeper Insight:
These breakthroughs attack quantum computing from two sides: scalable manufacturing and high-capacity qubits. When these trends converge, practical quantum computing could shift from test-bench to real-world application.
AI Actress Tilly Norwood In Negotiations with Talent Agencies
An AI-generated actress, Tilly Norwood, is in talks with several traditional talent agencies. Multiple agencies in Hollywood have publicly confirmed interest, though some top firms (like Gersh and WME) have stated they are not pursuing AI talent at this time. Her creators are pitching her for roles in film and advertising, sparking backlash from human actors and agents.
Deeper Insight:
This could mark the beginning of AI-native talent entering Hollywood. If audiences embrace synthetic performers with followings, studios and agencies may normalize them despite resistance from the acting community.
California Passes SB 53, First Frontier Model Transparency Law
Governor Gavin Newsom signed SB 53, requiring AI developers who spend more than $100 million on training to publish safety frameworks, report critical incidents, and maintain whistleblower channels. Anthropic supported the bill, while Meta and OpenAI opposed it.
Deeper Insight:
This law sets a precedent for U.S. AI regulation, mirroring parts of the EU AI Act. While companies could relocate to avoid compliance, California’s influence means other states may follow, reshaping governance for frontier AI models.
Did You Miss A Show Last Week?
Enjoy the replays on YouTube or take us with you in podcast form on Apple Podcasts or Spotify.
